A fitness club today is a facility or organization designed to provide a variety of health and fitness services to its members. Modern fitness clubs offer a wide range of amenities, programs, and equipment to cater to different fitness levels and interests.
Key components of a contemporary fitness club include:
- Gym Equipment:
- Cardio Machines: Treadmills, ellipticals, stationary bikes, rowing machines.
- Strength Training Equipment: Free weights, weight machines, resistance bands, kettlebells.
- Functional Training Areas: Space and equipment for exercises like CrossFit, TRX, and other bodyweight workouts.
- Cardio Machines: Treadmills, ellipticals, stationary bikes, rowing machines.
- Group Fitness Classes:
- Aerobics and Dance: Zumba, step aerobics, dance fitness.
- Mind-Body Classes: Yoga, Pilates, tai chi.
- High-Intensity Classes: HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training), boot camps, spin classes.
- Aerobics and Dance: Zumba, step aerobics, dance fitness.
- Personal Training and Coaching:
- Personal Trainers: Certified professionals who offer one-on-one training sessions, create personalized workout plans, and provide motivation and support.
- Health Coaches: Professionals who offer guidance on nutrition, lifestyle changes, and overall wellness.
- Personal Trainers: Certified professionals who offer one-on-one training sessions, create personalized workout plans, and provide motivation and support.
- Specialized Programs:
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Services for injury recovery and physical therapy sessions.
- Weight Management: Programs focused on weight loss or muscle gain through diet and exercise.
- Sports-Specific Training: Training tailored for athletes or specific sports.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Services for injury recovery and physical therapy sessions.
- Wellness and Spa Services:
- Massage Therapy: Various types of massages for relaxation and muscle recovery.
- Sauna and Steam Rooms: Facilities for relaxation and detoxification.
- Hydrotherapy Pools: Pools designed for therapeutic purposes.
- Massage Therapy: Various types of massages for relaxation and muscle recovery.
- Nutritional Guidance:
- Dietitians and Nutritionists: Experts who provide personalized nutrition plans and dietary advice.
- Healthy Eating Workshops: Classes and seminars on nutrition and healthy eating habits.
- Dietitians and Nutritionists: Experts who provide personalized nutrition plans and dietary advice.
- Technological Integration:
- Fitness Apps and Wearables: Tools for tracking workouts, progress, and health metrics.
- Virtual Classes and Training: Online workout classes and virtual coaching sessions.
- Interactive Equipment: Machines with screens offering guided workouts, virtual routes, and performance tracking.
- Fitness Apps and Wearables: Tools for tracking workouts, progress, and health metrics.
- Community and Social Support:
- Member Events and Challenges: Competitions, fitness challenges, and social events to foster a sense of community.
- Support Groups and Forums: Online and in-person groups for motivation and accountability.
- Member Events and Challenges: Competitions, fitness challenges, and social events to foster a sense of community.
- Convenience and Accessibility:
- 24/7 Access: Many fitness clubs offer round-the-clock access for members.
- Multiple Locations: Chain fitness clubs often provide access to various locations.
- Childcare Services: On-site childcare facilities to accommodate parents.
- 24/7 Access: Many fitness clubs offer round-the-clock access for members.
Modern fitness clubs aim to provide a comprehensive approach to health and fitness, focusing on physical, mental, and social well-being. They cater to a diverse range of fitness goals, from general health maintenance to specific athletic training, making them a versatile option for individuals seeking to improve their overall wellness.
The history of fitness clubs
The history of fitness clubs traces back to ancient civilizations and has evolved significantly over time, reflecting changes in societal values, scientific understanding of health, and technological advancements. Here’s an overview of their emergence and development:
Ancient Civilizations
- Ancient Greece and Rome:
- Gymnasiums: In Ancient Greece, gymnasiums were public spaces for both physical and intellectual education. They focused on physical training for men, particularly athletes training for the Olympic Games.
- Roman Baths: The Romans incorporated physical exercise into their routine through activities at public baths, which included areas for wrestling and weightlifting.
- Gymnasiums: In Ancient Greece, gymnasiums were public spaces for both physical and intellectual education. They focused on physical training for men, particularly athletes training for the Olympic Games.
- China and India:
- Martial Arts and Yoga: Physical fitness was also emphasized in ancient China and India through practices like martial arts and yoga, both of which aimed to enhance physical and mental well-being.
- Martial Arts and Yoga: Physical fitness was also emphasized in ancient China and India through practices like martial arts and yoga, both of which aimed to enhance physical and mental well-being.
18th and 19th Centuries: The Birth of Modern Fitness Culture
- Gymnastics and Physical Education:
- Germany and Sweden: The 18th and 19th centuries saw the development of gymnastics in Germany by Johann Guts Muths and Friedrich Jahn, and in Sweden by Pehr Henrik Ling. These movements emphasized systematic physical education.
- Physical Culture Movement: This movement, originating in Europe and spreading to North America, emphasized the importance of physical fitness and led to the establishment of numerous gymnasiums and athletic clubs.
- Germany and Sweden: The 18th and 19th centuries saw the development of gymnastics in Germany by Johann Guts Muths and Friedrich Jahn, and in Sweden by Pehr Henrik Ling. These movements emphasized systematic physical education.
- YMCA and Public Gyms:
- Young Men’s Christian Association (YMCA): Founded in London in 1844, the YMCA became instrumental in promoting physical fitness. The YMCA established gymnasiums and offered physical education classes, which laid the groundwork for modern fitness clubs.
- Young Men’s Christian Association (YMCA): Founded in London in 1844, the YMCA became instrumental in promoting physical fitness. The YMCA established gymnasiums and offered physical education classes, which laid the groundwork for modern fitness clubs.
Early 20th Century: Formalization and Commercialization
- Physical Fitness Boom:
- Military Influence: The World Wars highlighted the importance of physical fitness for military readiness, leading to increased public interest in physical conditioning.
- Public Figures: Influential figures like Jack LaLanne in the U.S. popularized physical fitness through television programs and opened some of the first modern health clubs.
- Military Influence: The World Wars highlighted the importance of physical fitness for military readiness, leading to increased public interest in physical conditioning.
- Fitness Centers and Clubs:
- First Health Clubs: In the 1930s and 1940s, health clubs began to emerge, offering more structured environments for exercise. Vic Tanny’s gyms, which opened in the 1940s and 1950s, are considered some of the first commercial fitness centers.
- First Health Clubs: In the 1930s and 1940s, health clubs began to emerge, offering more structured environments for exercise. Vic Tanny’s gyms, which opened in the 1940s and 1950s, are considered some of the first commercial fitness centers.
Late 20th Century: Expansion and Diversification
- Aerobics and Group Fitness:
- Aerobics Craze: In the 1970s and 1980s, the aerobics movement, spearheaded by figures like Jane Fonda and Richard Simmons, led to the proliferation of group fitness classes and the establishment of numerous aerobics studios.
- Aerobics Craze: In the 1970s and 1980s, the aerobics movement, spearheaded by figures like Jane Fonda and Richard Simmons, led to the proliferation of group fitness classes and the establishment of numerous aerobics studios.
- Fitness Chains:
- Expansion of Chains: Companies like Gold’s Gym (founded in 1965) and 24 Hour Fitness (founded in 1983) expanded rapidly, creating large networks of fitness clubs offering standardized services and equipment.
- Expansion of Chains: Companies like Gold’s Gym (founded in 1965) and 24 Hour Fitness (founded in 1983) expanded rapidly, creating large networks of fitness clubs offering standardized services and equipment.
- Diverse Offerings:
- Specialized Classes and Personal Training: The late 20th century saw the rise of specialized fitness classes (e.g., spinning, yoga, Pilates) and the professionalization of personal training.
- Specialized Classes and Personal Training: The late 20th century saw the rise of specialized fitness classes (e.g., spinning, yoga, Pilates) and the professionalization of personal training.
21st Century: Technological Integration and Holistic Wellness
- Technology and Fitness:
- Digital Fitness: The integration of technology in fitness has led to the rise of fitness apps, wearables, and virtual classes, making fitness more accessible and personalized.
- Smart Equipment: Modern gyms feature advanced equipment with digital interfaces that track performance and provide interactive workouts.
- Digital Fitness: The integration of technology in fitness has led to the rise of fitness apps, wearables, and virtual classes, making fitness more accessible and personalized.
- Holistic Approach:
- Wellness and Recovery: Contemporary fitness clubs often include wellness services such as massage therapy, nutritional counseling, and mental health support.
- Community and Experience: There is a growing focus on creating community-oriented spaces that offer a comprehensive fitness experience, including social events and member engagement activities.
- Wellness and Recovery: Contemporary fitness clubs often include wellness services such as massage therapy, nutritional counseling, and mental health support.
- Boutique Fitness Studios:
- Niche Markets: Boutique studios offering specialized workouts (e.g., HIIT, barre, CrossFit) have become popular, emphasizing a more personalized and community-driven approach.
- Niche Markets: Boutique studios offering specialized workouts (e.g., HIIT, barre, CrossFit) have become popular, emphasizing a more personalized and community-driven approach.
The evolution of fitness clubs from ancient gymnasiums to modern wellness centers reflects changing societal attitudes towards health and fitness. Today’s fitness clubs are diverse and multifaceted, catering to a wide range of fitness needs and preferences, and are an integral part of the health and wellness industry.
Alternatives to fitness clubs
There are many alternatives to fitness clubs, each offering unique benefits depending on personal preferences, fitness goals, and lifestyle. Here are some popular alternatives:
1. Home Workouts
- Equipment-Based: Use of home fitness equipment such as treadmills, stationary bikes, dumbbells, resistance bands, and home gym systems.
- Bodyweight Exercises: Exercises like push-ups, squats, lunges, and planks that require no equipment.
- Online Classes and Apps: Subscription-based services and apps like Peloton, Beachbody On Demand, and Nike Training Club offer guided workouts and programs.
2. Outdoor Activities
- Running and Jogging: Accessible and low-cost, suitable for various fitness levels.
- Cycling: Can be done solo or in groups, with road biking, mountain biking, and leisure cycling options.
- Hiking: Combines cardiovascular exercise with the enjoyment of nature.
- Swimming: Available in community pools, lakes, and the ocean, offering a full-body workout.
3. Sports and Recreational Activities
- Team Sports: Soccer, basketball, volleyball, and other team sports provide cardiovascular exercise and social interaction.
- Individual Sports: Tennis, golf, martial arts, and other individual sports can improve fitness and skill levels.
- Recreational Activities: Activities like rock climbing, dancing, and kayaking provide fitness benefits while being enjoyable hobbies.
4. Yoga and Pilates Studios
- Specialized Studios: Offer a variety of classes catering to different skill levels and goals, from relaxation and flexibility to strength and conditioning.
- Online Classes: Many studios and instructors offer virtual classes, making it easy to practice at home.
5. Community Centers and Public Facilities
- Local Gyms: Community centers often have basic gym facilities and offer classes at lower costs.
- Parks and Recreation Departments: Provide access to sports fields, courts, swimming pools, and organized fitness programs.
6. Personal Trainers and Coaches
- In-Person Training: Hiring a personal trainer for one-on-one sessions tailored to your fitness goals.
- Virtual Training: Online coaching and virtual personal training sessions, offering flexibility and convenience.
7. Workplace Wellness Programs
- On-Site Gyms: Some companies provide gym facilities within the workplace.
- Fitness Challenges and Group Classes: Organized fitness activities and challenges to promote health among employees.
- Health Incentives: Programs that offer incentives for achieving fitness goals, such as discounted gym memberships or health insurance rebates.
8. Dance and Movement Classes
- Dance Studios: Offering classes in styles like ballet, jazz, hip-hop, ballroom, and more.
- Group Dance Fitness: Classes like Zumba, barre, and dance aerobics that combine dance with fitness.
9. Online Fitness Communities
- Virtual Challenges and Competitions: Participate in online fitness challenges and virtual races.
- Support Groups and Forums: Join online communities for motivation, tips, and support from like-minded individuals.
10. Alternative and Holistic Practices
- Tai Chi and Qigong: Low-impact practices that focus on balance, flexibility, and mental wellness.
- Meditation and Mindfulness: Programs that emphasize mental health and stress reduction, often complementing physical fitness routines.
These alternatives to fitness clubs cater to a wide range of preferences and fitness levels, providing flexibility, convenience, and often a lower cost. Whether you prefer working out at home, enjoying the outdoors, participating in sports, or exploring new activities, there are many ways to stay active and healthy without a traditional gym membership.
The distribution of fitness clubs around the world.
The distribution of fitness clubs around the world varies based on factors such as economic development, cultural attitudes towards fitness, urbanization, and regional health trends. Here’s an overview of how fitness clubs are distributed globally:
North America
- United States:
- High Density: The U.S. has one of the highest concentrations of fitness clubs, with a strong culture of gym membership and a wide range of options from budget gyms to high-end fitness centers.
- Chains and Franchises: Popular chains like Planet Fitness, 24 Hour Fitness, and Equinox have numerous locations across the country.
- Boutique Studios: There is a significant presence of boutique fitness studios offering specialized classes such as spinning, yoga, and HIIT.
- High Density: The U.S. has one of the highest concentrations of fitness clubs, with a strong culture of gym membership and a wide range of options from budget gyms to high-end fitness centers.
- Canada:
- Growing Market: Fitness club membership is increasing, with both large chains and boutique studios becoming more common.
- Diverse Offerings: Facilities offer a variety of services, including traditional gyms, wellness centers, and outdoor fitness programs.
- Growing Market: Fitness club membership is increasing, with both large chains and boutique studios becoming more common.
Europe
- Western Europe:
- Established Market: Countries like the UK, Germany, France, and the Netherlands have well-established fitness club industries with a mix of large chains (e.g., PureGym, Fitness First) and independent gyms.
- Diverse Options: There is a wide range of fitness clubs, from affordable options to luxury wellness centers, and a growing trend of boutique studios.
- Established Market: Countries like the UK, Germany, France, and the Netherlands have well-established fitness club industries with a mix of large chains (e.g., PureGym, Fitness First) and independent gyms.
- Eastern Europe:
- Emerging Market: Fitness culture is growing, with increasing numbers of fitness clubs, particularly in urban areas.
- Focus on Modern Facilities: Many new fitness clubs offer state-of-the-art equipment and facilities, reflecting a rising demand for quality fitness services.
- Emerging Market: Fitness culture is growing, with increasing numbers of fitness clubs, particularly in urban areas.
Asia
- East Asia:
- High Population Density: Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea have rapidly growing fitness industries, especially in major cities.
- Large Chains and Local Gyms: Both international chains (e.g., Anytime Fitness, Gold’s Gym) and local brands are popular.
- Technological Integration: There is a strong emphasis on integrating technology with fitness, including virtual classes and fitness apps.
- High Population Density: Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea have rapidly growing fitness industries, especially in major cities.
- Southeast Asia:
- Growing Awareness: Countries like Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand are seeing increasing interest in fitness and wellness, with new fitness clubs and boutique studios opening.
- Expat Influence: The fitness culture is often influenced by expatriates, leading to diverse offerings and high standards in fitness facilities.
- Growing Awareness: Countries like Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand are seeing increasing interest in fitness and wellness, with new fitness clubs and boutique studios opening.
- South Asia:
- Emerging Market: In countries like India, fitness clubs are becoming more common, especially in urban centers.
- Health and Wellness Focus: There is a growing trend towards holistic wellness, combining traditional practices like yoga with modern fitness regimes.
- Emerging Market: In countries like India, fitness clubs are becoming more common, especially in urban centers.
Middle East
- High-Income Countries:
- Luxury Fitness Clubs: In countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia, there is a trend towards high-end fitness clubs offering luxurious amenities.
- Rapid Growth: The fitness industry is expanding rapidly, with a focus on catering to both local populations and expatriates.
- Luxury Fitness Clubs: In countries like the UAE and Saudi Arabia, there is a trend towards high-end fitness clubs offering luxurious amenities.
Africa
- South Africa:
- Established Market: South Africa has a relatively well-developed fitness industry, with a mix of local gyms and international chains.
- Increasing Health Awareness: Growing awareness of health and fitness is driving demand for fitness services.
- Established Market: South Africa has a relatively well-developed fitness industry, with a mix of local gyms and international chains.
- Other African Regions:
- Emerging Markets: Fitness clubs are less common but are growing in major cities across countries like Kenya, Nigeria, and Egypt.
- Focus on Affordability: Many new fitness clubs aim to be accessible and affordable to cater to a broader population.
- Emerging Markets: Fitness clubs are less common but are growing in major cities across countries like Kenya, Nigeria, and Egypt.
Latin America
- Brazil:
- Large Market: Brazil has a vibrant fitness culture, with a high number of fitness clubs and a focus on bodybuilding and group fitness classes.
- Popular Chains: Brands like Smart Fit have a strong presence.
- Large Market: Brazil has a vibrant fitness culture, with a high number of fitness clubs and a focus on bodybuilding and group fitness classes.
- Other Countries:
- Growing Industry: Countries like Mexico, Argentina, and Colombia are seeing growth in the fitness industry, with an increasing number of gyms and fitness clubs.
- Cultural Influence: Local fitness trends often include activities like dance fitness (e.g., Zumba) and outdoor exercises.
- Growing Industry: Countries like Mexico, Argentina, and Colombia are seeing growth in the fitness industry, with an increasing number of gyms and fitness clubs.
Oceania
- Australia and New Zealand:
- High Penetration: Both countries have a well-established fitness culture with a high number of fitness clubs per capita.
- Diverse Offerings: A wide range of fitness clubs, from large chains (e.g., Fitness First) to boutique studios, cater to different fitness preferences.
- High Penetration: Both countries have a well-established fitness culture with a high number of fitness clubs per capita.
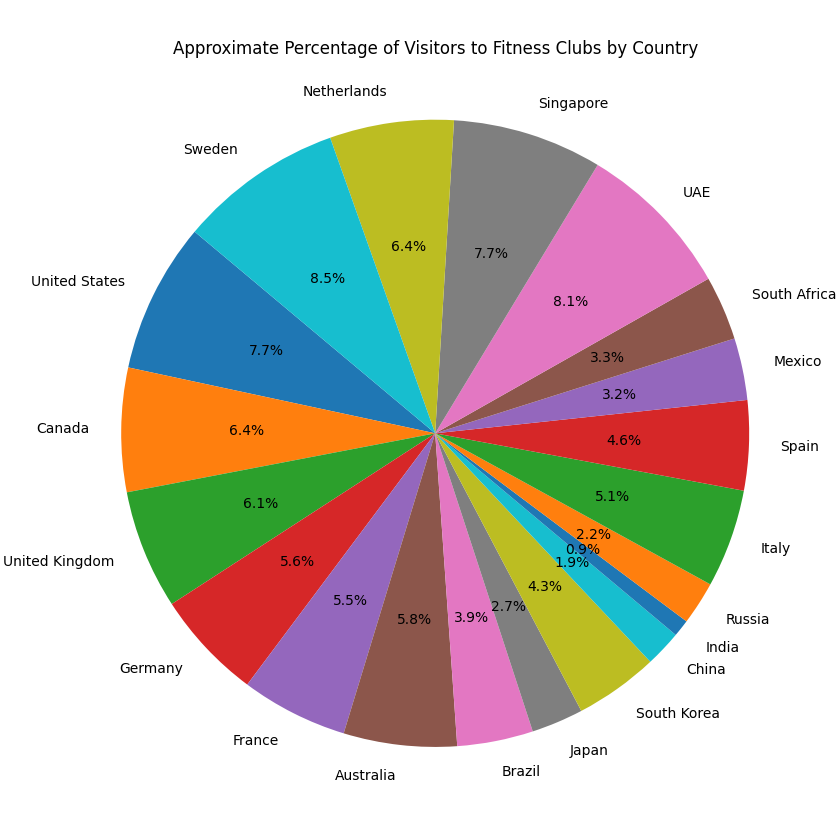
Here’s a table showing an approximate percentage of visitors to fitness clubs in relation to the population of various countries. These percentages are estimates based on available data and may vary:
| Country | Population (2023, millions) | Fitness Club Visitors (millions) | Percentage of Population (%) |
| United States | 331.9 | 64.2 | 19.4 |
| Canada | 38.2 | 6.1 | 16.0 |
| United Kingdom | 67.3 | 10.4 | 15.4 |
| Germany | 83.2 | 11.7 | 14.1 |
| France | 65.4 | 9.0 | 13.8 |
| Australia | 26.1 | 3.8 | 14.6 |
| Brazil | 213.4 | 21.0 | 9.8 |
| Japan | 126.1 | 8.5 | 6.7 |
| South Korea | 51.7 | 5.6 | 10.8 |
| China | 1444.2 | 68.0 | 4.7 |
| India | 1391.9 | 31.0 | 2.2 |
| Russia | 143.4 | 8.1 | 5.6 |
| Italy | 59.0 | 7.5 | 12.7 |
| Spain | 47.4 | 5.5 | 11.6 |
| Mexico | 127.8 | 10.2 | 8.0 |
| South Africa | 60.1 | 5.0 | 8.3 |
| UAE | 9.8 | 2.0 | 20.4 |
| Singapore | 5.7 | 1.1 | 19.3 |
| Netherlands | 17.5 | 2.8 | 16.0 |
| Sweden | 10.4 | 2.2 | 21.2 |
Notes:
- Population data is based on estimates for 2023.
- Fitness club visitors are estimates and may include members who visit regularly, occasionally, or hold memberships without frequent visits.
- These percentages are approximations and may differ based on the specific definitions of “fitness club visitors” and the methodology used in surveys.
This table provides a general overview of fitness club penetration in various countries, highlighting how prevalent gym membership and fitness club visits are relative to the total population.
Demographic Profile of Fitness Club Visitors
A typical fitness club visitor can be described through various demographic attributes such as age, gender, income level, education, and fitness goals. Here’s a detailed profile based on these factors:
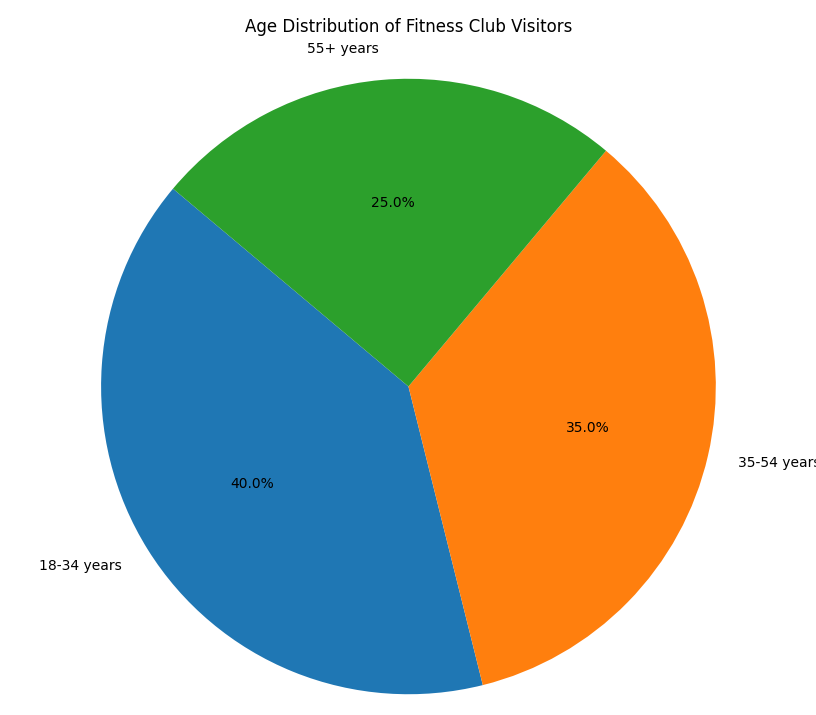
- Age:
- Young Adults (18-34 years): This age group forms a significant portion of fitness club members. They are often motivated by aesthetic goals, such as building muscle or losing weight, and are more likely to participate in high-intensity workouts and group classes.
- Middle-Aged Adults (35-54 years): Another large demographic, focusing on maintaining fitness levels, weight management, and stress relief. This group often balances work and family responsibilities.
- Older Adults (55+ years): While a smaller percentage, this group is growing as more seniors recognize the importance of fitness for health and longevity. They often engage in low-impact activities like yoga, swimming, and gentle strength training.
- Young Adults (18-34 years): This age group forms a significant portion of fitness club members. They are often motivated by aesthetic goals, such as building muscle or losing weight, and are more likely to participate in high-intensity workouts and group classes.
- Gender:
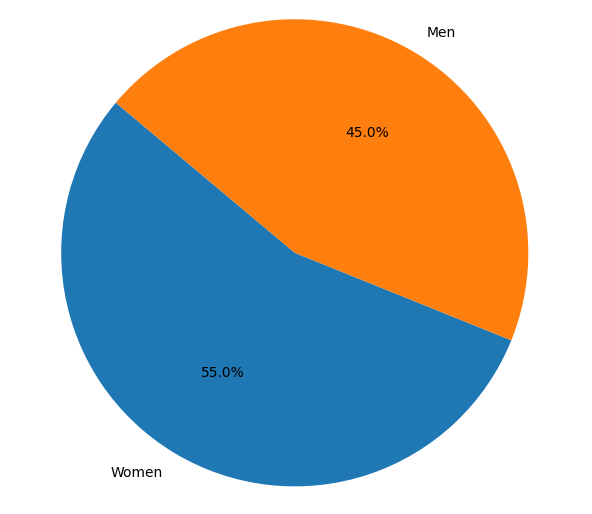
- Women: Women tend to participate more in group fitness classes such as aerobics, yoga, Pilates, and dance fitness. They often prioritize weight management, overall health, and social aspects of fitness.
- Men: Men are more likely to focus on strength training and bodybuilding. They frequently use free weights and resistance machines and may also participate in competitive sports and high-intensity workouts.
- Women: Women tend to participate more in group fitness classes such as aerobics, yoga, Pilates, and dance fitness. They often prioritize weight management, overall health, and social aspects of fitness.
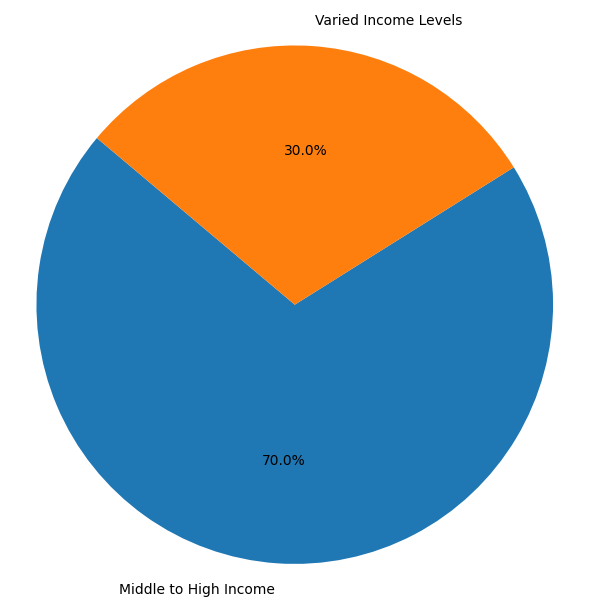
- Income Level:
- Middle to High Income: Fitness club members typically fall within middle to higher income brackets. Membership fees, especially for high-end and boutique gyms, can be substantial, thus attracting individuals with disposable income.
- Varied Income Levels: Budget gyms and community centers cater to a broader range of income levels, making fitness more accessible to different socioeconomic groups.
- Middle to High Income: Fitness club members typically fall within middle to higher income brackets. Membership fees, especially for high-end and boutique gyms, can be substantial, thus attracting individuals with disposable income.
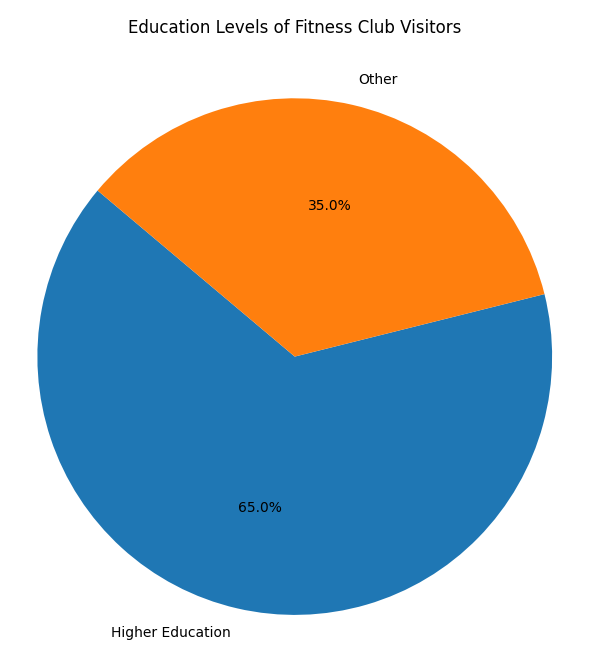
- Education:
- Higher Education Levels: Individuals with higher education levels are often more aware of the benefits of regular exercise and are more likely to invest in gym memberships. They may also have more flexible work schedules that allow for regular gym visits.
- Higher Education Levels: Individuals with higher education levels are often more aware of the benefits of regular exercise and are more likely to invest in gym memberships. They may also have more flexible work schedules that allow for regular gym visits.
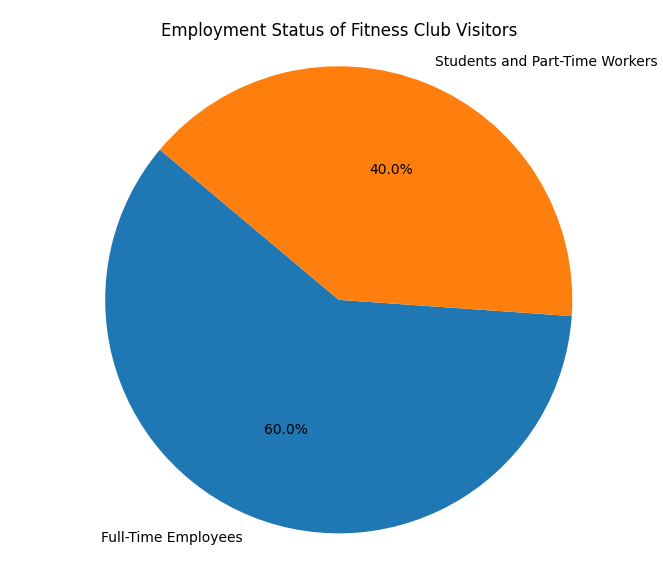
- Employment Status:
- Full-Time Employees: Many fitness club visitors are full-time workers who visit gyms before or after work, or during lunch breaks.
- Students and Part-Time Workers: Students and part-time workers also constitute a significant portion, often opting for gyms with flexible hours or those located near educational institutions.
- Full-Time Employees: Many fitness club visitors are full-time workers who visit gyms before or after work, or during lunch breaks.
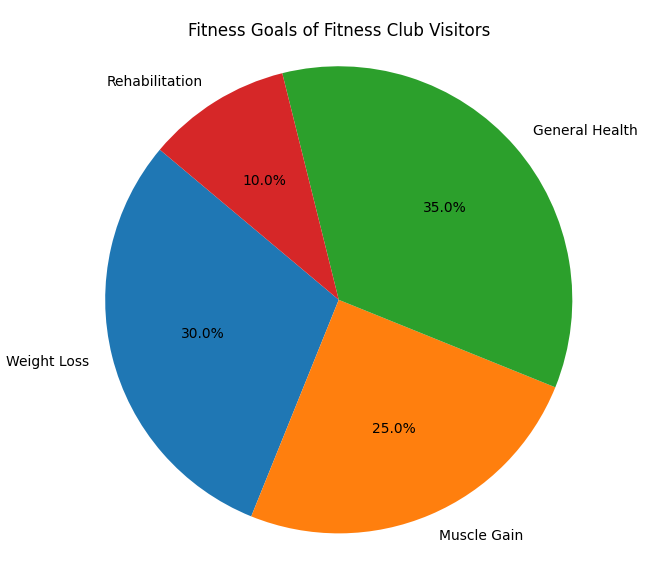
- Fitness Goals:
- Weight Loss: A common goal among fitness club members, often driving membership and participation in cardio and group fitness classes.
- Muscle Gain and Bodybuilding: Predominantly among younger men and some women, focusing on strength training and resistance exercises.
- General Health and Wellness: Includes improving cardiovascular health, managing stress, and enhancing overall quality of life.
- Rehabilitation and Injury Prevention: Some members join fitness clubs for access to specialized equipment and programs designed for injury recovery and prevention.
- Weight Loss: A common goal among fitness club members, often driving membership and participation in cardio and group fitness classes.
- Geographic Location:
- Urban Areas: Higher concentration of fitness club members in cities due to greater availability of gyms, higher population density, and more disposable income.
- Suburban Areas: Also have a significant number of fitness clubs, catering to families and individuals looking for convenient, local options.
- Rural Areas: Fewer fitness clubs, with members often traveling longer distances to access facilities or using local community centers.
- Urban Areas: Higher concentration of fitness club members in cities due to greater availability of gyms, higher population density, and more disposable income.
So a typical fitness club visitor can be described as a young to middle-aged adult with a moderate to high income level, likely to be employed full-time and educated. They join fitness clubs for various reasons, including weight loss, muscle gain, general health, and wellness. Fitness clubs cater to diverse needs, offering a wide range of services and facilities to accommodate different demographics and fitness goals.
The number of visitors to fitness clubs typically changes throughout the year, influenced by seasonal trends, holidays, and cultural events. Here’s a detailed look at how these factors affect fitness club attendance:
Seasonal Trends
- New Year’s Resolutions (January-March):
- Peak Period: Many people set fitness goals as part of their New Year’s resolutions, leading to a significant increase in gym memberships and attendance in January and February.
- Motivation Boost: Fitness clubs often run promotions and discounts to attract new members during this period.
- Peak Period: Many people set fitness goals as part of their New Year’s resolutions, leading to a significant increase in gym memberships and attendance in January and February.
- Spring (April-June):
- Moderate Activity: Attendance generally remains steady as people prepare for summer, focusing on fitness goals like weight loss and muscle toning.
- Outdoor Activities: Some members may reduce gym visits in favor of outdoor exercises as the weather improves.
- Moderate Activity: Attendance generally remains steady as people prepare for summer, focusing on fitness goals like weight loss and muscle toning.
- Summer (July-September):
- Decline in Attendance: Gym visits often decline as people go on vacations and engage in outdoor activities.
- Seasonal Programs: Fitness clubs may offer summer-specific programs, like outdoor boot camps, to retain members.
- Decline in Attendance: Gym visits often decline as people go on vacations and engage in outdoor activities.
- Fall (October-December):
- Increase in Attendance: As vacations end and routines normalize, gym attendance often rises.
- Pre-Holiday Push: There is usually a spike in attendance as people try to get in shape before the holiday season.
- Increase in Attendance: As vacations end and routines normalize, gym attendance often rises.
Holidays and Cultural Events
- Holiday Season (November-December):
- Fluctuating Attendance: Gym visits can be inconsistent due to holiday preparations, travel, and festivities.
- Promotional Offers: Fitness clubs may offer special holiday promotions to attract and retain members during this period.
- Fluctuating Attendance: Gym visits can be inconsistent due to holiday preparations, travel, and festivities.
- Back-to-School (August-September):
- Routine Resumption: Parents and students returning to a regular schedule often leads to a stabilization or increase in gym attendance.
- Routine Resumption: Parents and students returning to a regular schedule often leads to a stabilization or increase in gym attendance.
Weekly and Daily Patterns
- Weekdays vs. Weekends:
- Higher Weekday Attendance: Many people prefer to work out before or after work on weekdays, leading to higher attendance.
- Lower Weekend Attendance: Weekend visits may drop as people engage in leisure activities or travel.
- Higher Weekday Attendance: Many people prefer to work out before or after work on weekdays, leading to higher attendance.
- Time of Day:
- Peak Hours: Early morning, lunchtime, and after work are typically the busiest times in fitness clubs.
- Off-Peak Hours: Mid-morning and mid-afternoon usually see fewer visitors.
- Peak Hours: Early morning, lunchtime, and after work are typically the busiest times in fitness clubs.
Special Promotions and Events
- Fitness Challenges:
- Boost in Attendance: Fitness clubs often organize challenges and competitions that encourage higher attendance and member engagement.
- Boost in Attendance: Fitness clubs often organize challenges and competitions that encourage higher attendance and member engagement.
- New Class Introductions:
- Increased Interest: Launching new classes or programs can attract more visitors, especially if they cater to current fitness trends.
- Increased Interest: Launching new classes or programs can attract more visitors, especially if they cater to current fitness trends.
The business model of a fitness club
The business model of a fitness club typically revolves around membership fees, additional services (such as personal training, group classes, and retail sales), and sometimes ancillary revenue streams like cafe sales or renting out space for events. Let’s break down some key aspects:
- Membership Fees: Most fitness clubs offer various membership tiers with different pricing structures (monthly, quarterly, annually). Members pay these fees for access to the gym facilities, which often include cardio and strength equipment, group exercise classes, locker rooms, and sometimes additional amenities like pools or saunas.
- Additional Services: Many fitness clubs generate extra revenue by offering personal training sessions, group fitness classes (such as yoga or spin classes), nutritional counseling, and other specialized services for an additional fee.
- Retail Sales: Some fitness clubs sell merchandise like branded apparel, supplements, and fitness accessories to their members, providing an additional revenue stream.
- Ancillary Revenue: Some clubs have cafes, smoothie bars, or juice bars where members can purchase refreshments. Additionally, some fitness clubs rent out space for events like fitness competitions, workshops, or parties, which can generate extra income.
Profitability can vary widely depending on factors such as location, size, competition, pricing strategy, and operational efficiency. Successful fitness clubs often focus on retaining members through excellent customer service, maintaining high-quality facilities, and offering a variety of programs to meet diverse fitness needs.
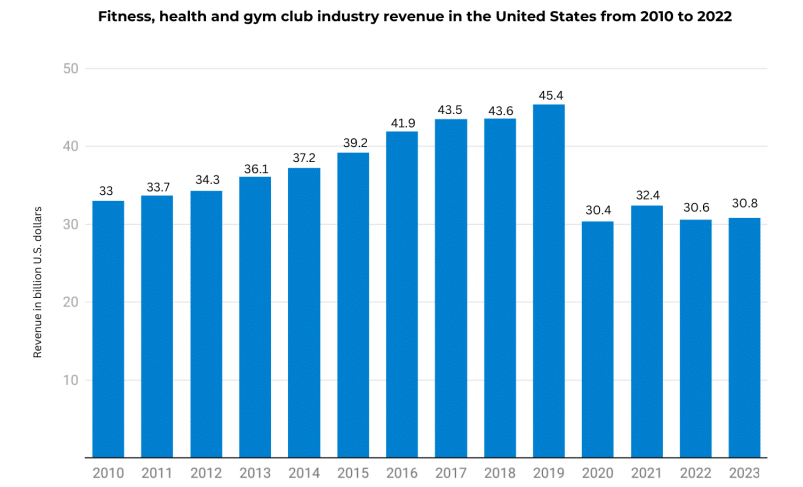
As for global income, the fitness industry generates billions of dollars in revenue annually. According to the International Health, Racquet & Sportsclub Association (IHRSA), the global health club industry was valued at $96.7 billion in 2019, with over 184 million members worldwide, $104.05 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow from $112.17 billion in 2023 to $202.78 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 8.83% during the forecast period. However, it’s essential to note that these figures can fluctuate due to economic conditions, trends in consumer behavior, and other factors.
Some of the most famous fitness clubs in the world include:
- Gold’s Gym: Founded in 1965 in Venice Beach, California, Gold’s Gym has become an iconic brand in the fitness industry. It has franchises and locations worldwide, catering to millions of members.
- 24 Hour Fitness: With over 400 clubs in the United States, 24 Hour Fitness is one of the largest fitness chains in the world. It offers a wide range of amenities and services, including group exercise classes, personal training, and state-of-the-art equipment.
- Equinox: Known for its luxurious amenities and upscale atmosphere, Equinox has gained popularity among affluent clientele. It offers high-end fitness facilities, spa services, and exclusive group fitness classes.
- Anytime Fitness: Anytime Fitness operates on a 24/7 access model, allowing members to work out at any time of day or night. With thousands of locations worldwide, it has built a reputation for convenience and accessibility.
- LA Fitness: LA Fitness boasts a large network of clubs across the United States and Canada, offering a variety of fitness equipment, group classes, and amenities like swimming pools and basketball courts.
As for the number of clients and income of these fitness clubs, specific data can vary and may not be publicly available for all clubs. However, these brands typically generate significant revenue through membership fees, additional services, and ancillary revenue streams like retail sales and cafe offerings. Their client base can range from tens of thousands to millions of members worldwide, depending on the size and popularity of the chain.

Fitness clubs and show business stars often have a symbiotic relationship, as many celebrities rely on fitness clubs and personal trainers to maintain their physical health and appearance. Additionally, some celebrities have even become involved in the fitness industry themselves by endorsing fitness products, launching their own workout programs, or investing in gym franchises. Here are a few examples:
- Celebrity Endorsements: Many fitness clubs and brands leverage the popularity of show business stars by having them endorse their products or services. Celebrities may appear in advertisements, social media campaigns, or promotional events to promote a particular gym chain, workout gear, or fitness program.
- Celebrity Trainers: Some high-profile celebrities work closely with personal trainers to achieve their fitness goals. These trainers may be well-known in the fitness industry and may even have their own gym or training studio catering to elite clientele.
- Celebrity-Owned Gyms: Some celebrities have taken their involvement in the fitness industry a step further by investing in or owning their own gym franchises. For example, Mark Wahlberg co-owns the F45 Training franchise, while David Beckham has invested in several gyms under the UFC Gym brand.
- Workout Programs: Several celebrities have developed their own workout programs or fitness DVDs, capitalizing on their fame to attract customers. These programs often incorporate elements of the celebrity’s personal fitness routine and may include workouts, meal plans, and motivational content.
Overall, the intersection of fitness clubs and show business stars highlights the influence of celebrities in shaping fitness trends and promoting a healthy lifestyle to their fans and followers.
Scientific research on the effectiveness of visiting fitness clubs and various types of physical activity is extensive and covers a wide range of topics. Here are some key points based on research findings:
- Overall Health Benefits: Numerous studies have demonstrated the positive effects of regular physical activity on overall health. Exercise can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and certain types of cancer. It also improves mental health by reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety and enhancing cognitive function.
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Aerobic or cardiovascular exercise, such as running, cycling, swimming, or using cardio machines like treadmills or ellipticals, is highly effective for improving cardiovascular health. It strengthens the heart, improves circulation, lowers blood pressure, and increases aerobic fitness.
- Strength Training: Resistance training, including weightlifting, bodyweight exercises, and using resistance machines, is essential for building muscle strength and endurance. It also improves bone density, posture, and metabolism. Research suggests that strength training is particularly beneficial for older adults in preventing age-related muscle loss and maintaining independence.
- Flexibility and Balance: Activities that improve flexibility, balance, and coordination, such as yoga, Pilates, and tai chi, are crucial for maintaining mobility and preventing falls, especially in older adults. These practices also promote relaxation, stress reduction, and mental well-being.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT involves alternating short bursts of intense exercise with brief periods of rest or lower-intensity activity. Research indicates that HIIT is an efficient way to improve cardiovascular fitness, burn calories, and boost metabolism in a shorter amount of time compared to traditional steady-state cardio workouts.
- Mind-Body Practices: Mind-body exercises like yoga and meditation not only improve physical health but also enhance mental resilience, mindfulness, and emotional well-being. These practices can reduce stress, improve sleep quality, and promote overall relaxation.
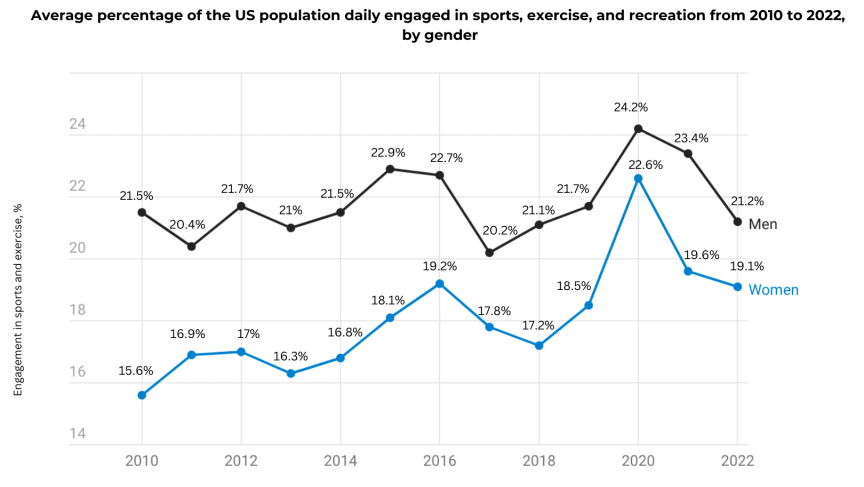
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of physical activity can vary depending on individual factors such as age, fitness level, health status, and personal preferences. A well-rounded fitness program typically includes a combination of cardiovascular exercise, strength training, flexibility work, and mind-body practices to reap the maximum health benefits. Additionally, consistency and adherence to an exercise routine are key factors in achieving and maintaining long-term health and fitness goals.
Client satisfaction with fitness club results can vary widely depending on individual factors such as their goals, commitment level, consistency, and the quality of the services provided by the club. Here are some factors that can contribute to client satisfaction:
- Achievement of Goals: Clients are more likely to be satisfied if they achieve the fitness goals they set out to accomplish, whether it’s weight loss, muscle gain, improved endurance, or overall health and well-being.
- Quality of Facilities and Equipment: Clients expect clean, well-maintained facilities with a variety of up-to-date equipment to support their workouts effectively. Access to amenities such as locker rooms, showers, and parking can also influence satisfaction.
- Effectiveness of Programs and Services: Fitness clubs that offer diverse programs, expert-led classes, personalized training sessions, and nutritional guidance are more likely to meet the diverse needs of their clients and contribute to their satisfaction.
- Supportive Staff: Friendly, knowledgeable staff members who provide excellent customer service, guidance, and encouragement can enhance the overall experience and satisfaction of clients.
- Community and Atmosphere: A positive, motivating atmosphere and a sense of community among members can contribute to client satisfaction by fostering accountability, camaraderie, and a supportive environment.
- Value for Money: Clients expect fair pricing and value for the fees they pay, considering factors such as the quality of services, amenities, and overall experience provided by the fitness club.
While many clients may be satisfied with their experiences at fitness clubs, it’s important to recognize that individual preferences and expectations can vary. Some clients may achieve great results and feel highly satisfied, while others may not see the desired outcomes or may have had negative experiences. Effective communication, ongoing feedback, and a commitment to continuous improvement can help fitness clubs enhance client satisfaction and loyalty over time.